Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
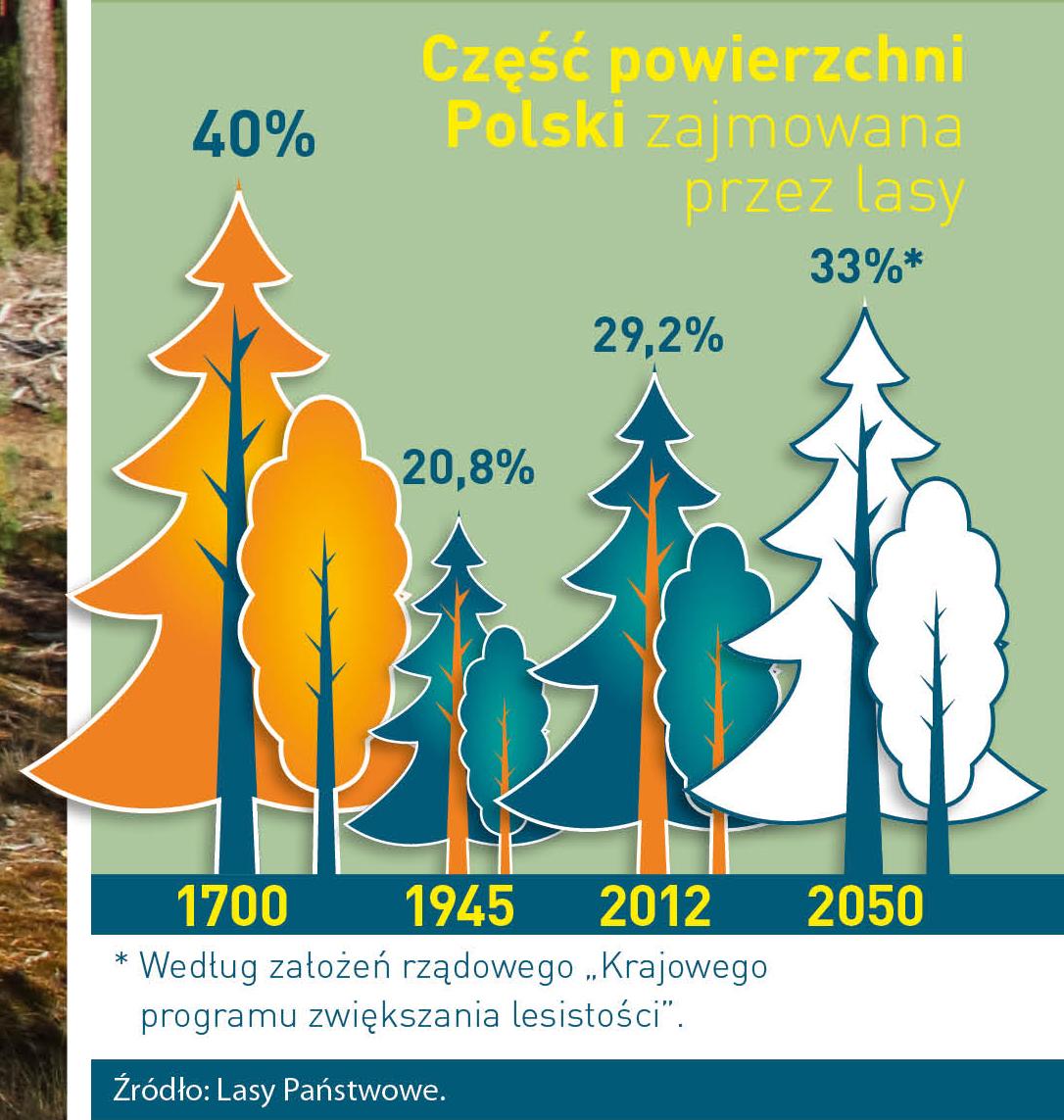
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Wkrótce rusza akcja „Wieniec”
Wkrótce rusza akcja „Wieniec”
Jest to już cykliczna akcja Straży Leśnej, prowadzona przy wsparciu sił Policji, Straży Granicznej oraz Państwowej Straży Łowieckiej.
Jej celem jest przeciwdziałanie i zwalczanie kłusownictwa oraz pozostałych przejawów tzw. szkodnictwa łowieckiego, kontrola legalności skupu i obrotu zwierzyną, a także egzekwowanie, głównie od osób trudniących się zbieraniem zrzutów poroży, zachowań zgodnych z obowiązującymi przepisami.
Działania strażników leśnych i pozostałych służb obejmą przede wszystkim patrolowanie terenów będących ostoją zwierzyny, obszarów zagrożonych kłusownictwem i odwiedzanych przez zbieraczy poroża. Podczas patroli będą sprawdzać czy zbieracze poroża nie wkraczają np. na tereny rezerwatów czy w miejsca objęte zakazem wstępu, czy swoimi działaniami nie płoszą zwierząt i nie narażają ich na stres. Przy okazji kontrolować będą czy w terenie nie są rozstawiane wnyki. Kontrole obejmą także punkty skupu dziczyzny i legalne pochodzenie mięsa.
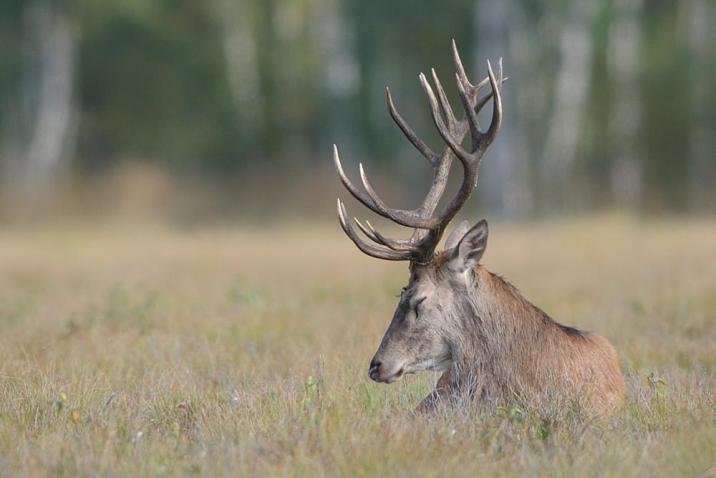
Poroże to twarda, kostna struktura, którą noszą samce krajowych jeleniowatych. Im większe i okazalsze tym lepiej świadczy o sile oraz możliwościach reprodukcyjnych samca. Oprócz funkcji reprezentacyjnej służy także jako broń podczas walk byków o samice. Po zakończeniu okresu godowego jest ono zrzucane. Proces zrzucania poroża odbywa się co roku – samiec gubi stare poroże, a w jego miejsce wyrasta nowe.
Zrzutami nazywamy poroże zgubione przez sarny, łosie, daniele i jelenie. Przełom lutego i marca ta czas, kiedy jelenie pozbywają się starego poroża. Jednocześnie to czas kiedy do lasu ruszają „łowcy zrzutów”.
Zgodnie z obowiązującym w Polsce prawem znalezione zrzuty możemy sobie zabrać jeśli zostały one znalezione na terenie lasów gospodarczych. Zbieranie zrzutów w rezerwatach i parkach narodowych jest nielegalne. Udając się do lasu na poszukiwanie zrzutów należy pamiętać również o miejscach, w których obowiązuje zakaz wstępu, mimo, że jest to las gospodarczy. Są to m.in. lasy do 4 m wysokości drzew czy tereny oznaczone jako „Ostoja zwierzyny”.
Nie wolno również tropić i płoszyć zwierząt aby zdobyć poroże. Niestety nie wszyscy zbieracze postępują etycznie. Tropią chmary jeleni, zmuszają je do ciągłego przemieszczania się co doprowadza do osłabienia zwierząt, którym i tak jest ciężko z uwagi na zimowe warunki i ograniczony dostęp do pożywienia.
O tym jak szukać zrzutów w lesie opowiada Zdobek w jednym z odcinków „Obliczy lasów:


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański